Controllable Person Image Synthesis with Attribute-Decomposed GAN
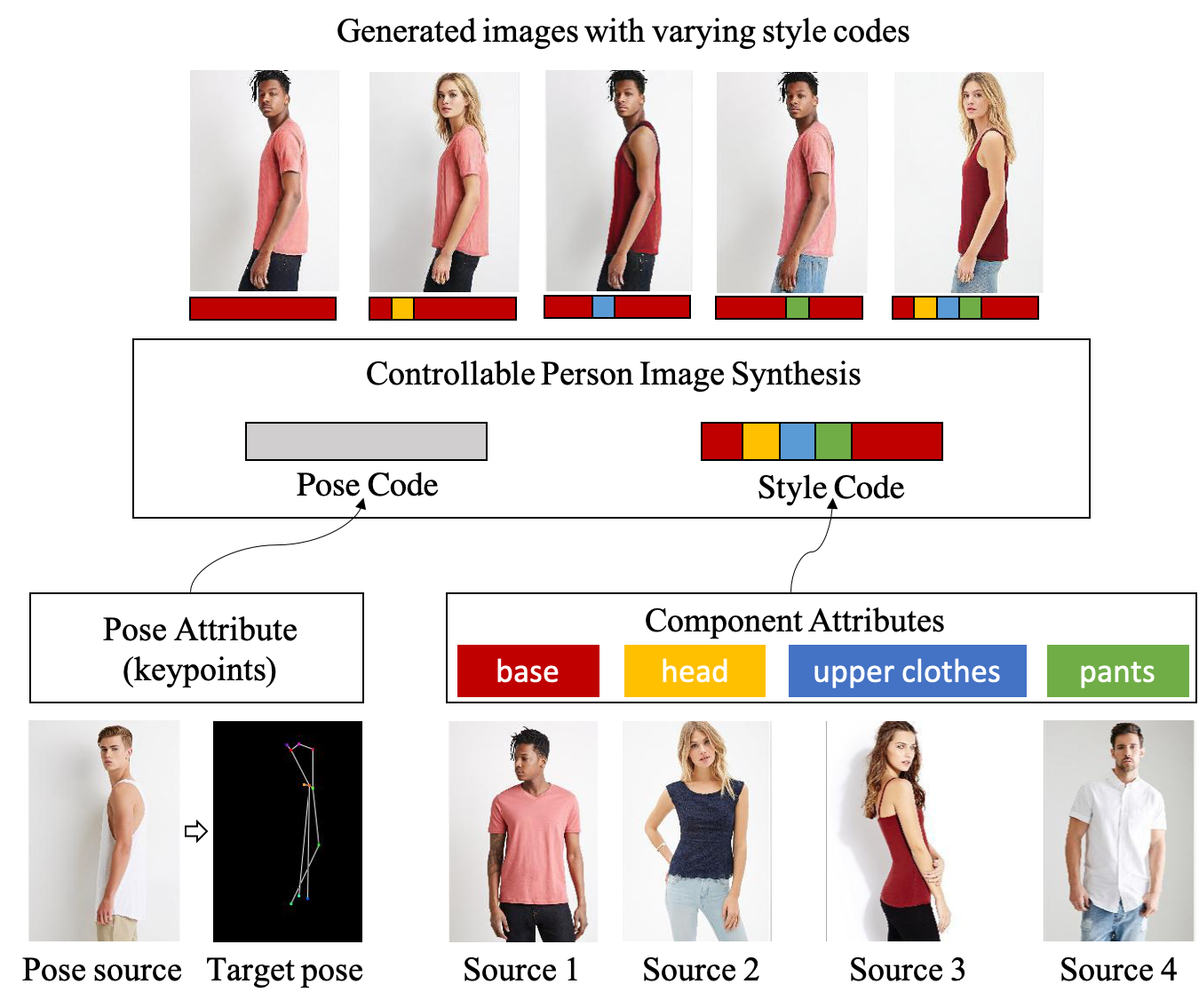
Fig.1 Controllable person image synthesis with desired human attributes provided by multiple source images. Human attributes including pose and component attributes are embedded into the latent space as the pose code and decomposed style code. Target person images can be generated in user control with editable style code.
Abstract
This paper introduces Attribute-Decomposed GAN, a novel generative model for controllable person image synthesis, which can produce realistic person images with desired human attributes (e.g., pose, head, upper clothes and pants) provided in various source inputs. The core idea of the proposed model is to embed human attributes into the latent space as independent codes and thus achieve flexible and continuous control of attributes via mixing and interpolation operations in explicit style representations. Specifically, a new architecture consisting of two encoding pathways with style block connections is proposed to decompose the original hard mapping into multiple more accessible subtasks. In source pathway, we further extract component layouts with an off-the-shelf human parser and feed them into a shared global texture encoder for decomposed latent codes. This strategy allows for the synthesis of more realistic output images and automatic separation of un-annotated attributes. Experimental results demonstrate the proposed methods superiority over the state of the art in pose transfer and its effectiveness in the brand-new task of component attributes transfer.
Network
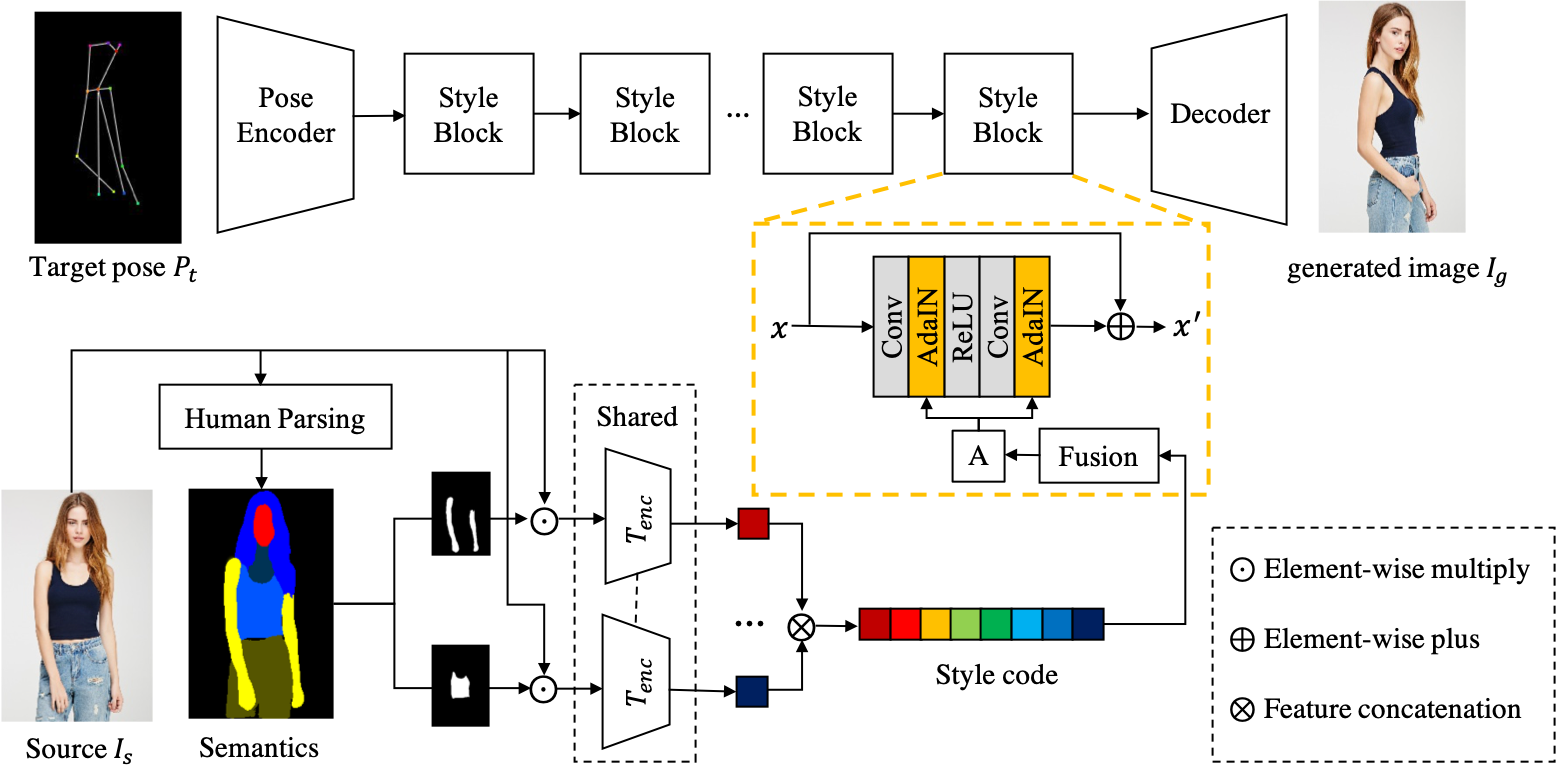
Fig.2 An overview of the network architecture of our generator.
Experimental Results
Component Attributes Transfer
| Source B: other component attributes |

| Source A: upper clothes | Results of combining A and B |
Pose Transfer

Citation
@inproceedings{men2020controllable, title={Controllable Person Image Synthesis with Attribute-Decomposed GAN}, author={Men, Yifang and Mao, Yiming and Jiang, Yuning and Ma, Wei-Ying and Lian, Zhouhui}, booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition}, year={2020} }